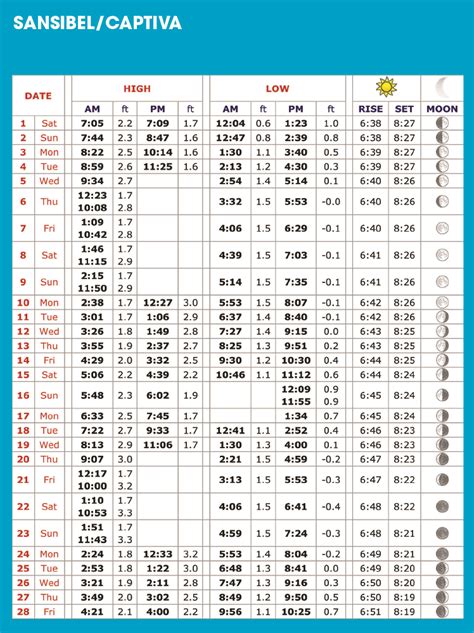
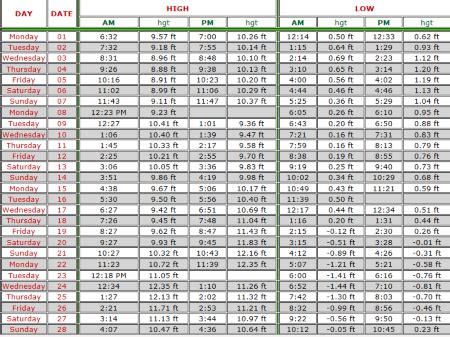
Located on the Gulf Coast of Florida, Sanibel Island is renowned for its shell-filled beaches, wildlife refuges, and pristine natural beauty. One of the key factors that influence the island's ecosystem and appeal to visitors is its tide schedule. The tidal patterns play a crucial role in shaping the shoreline, affecting the availability of certain marine species, and influencing the overall beach experience. Understanding the Sanibel Island tide schedule is essential for both residents and tourists looking to make the most of their time on the island.
Understanding Tides on Sanibel Island
Tides are the periodic rising and falling of the sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the Earth’s oceans. The interaction between these celestial bodies results in two main types of tides: semidiurnal and diurnal. Sanibel Island experiences a mixed semidiurnal tide, which means it has two high tides and two low tides each day, but the heights of the high tides and the depths of the low tides are not equal. This mixed pattern is due to the island’s geographical location in the Gulf of Mexico, where the tidal range is moderate.
Tidal Cycles and Patterns
The tidal cycle on Sanibel Island follows a predictable pattern, with the tide rising to its highest point (high tide) and then falling to its lowest point (low tide) over a period of approximately 12 hours and 25 minutes. This cycle is repeated throughout the day, resulting in the mixed semidiurnal tide pattern characteristic of the area. The height of the tide, or tidal range, varies significantly over the course of a month, with the most extreme tidal ranges occurring during the new moon and full moon phases, known as spring tides. Conversely, the least extreme tidal ranges happen during the quarter moon phases, known as neap tides.
| Tidal Phase | Tidal Range (Feet) |
|---|---|
| Spring Tide (New Moon) | 2.5 - 3.0 |
| Neap Tide (Quarter Moon) | 1.0 - 1.5 |
| Average Tide | 1.8 - 2.2 |
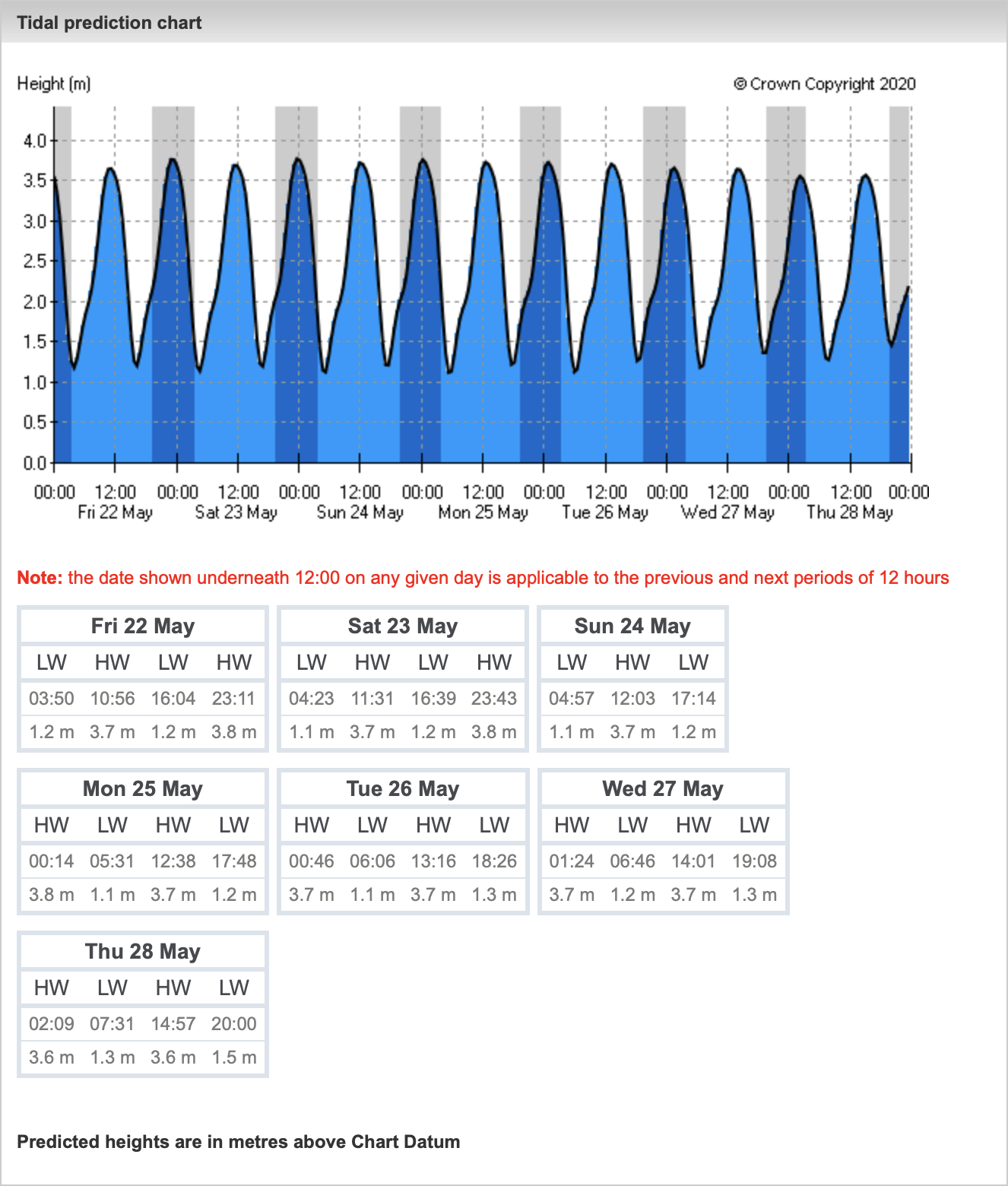
Practical Applications of the Tide Schedule
The Sanibel Island tide schedule has numerous practical applications for both leisure and conservation purposes. For beachgoers, knowing the tide times can help in planning the best moments to search for seashells, as the exposed beach during low tide offers a wider area to explore. For fishermen, the changing tides can signal the movement and feeding patterns of various fish species, increasing the chances of a successful catch. Furthermore, for conservation efforts, understanding the tidal patterns is essential for managing and protecting the island’s sensitive ecosystems, such as the mangrove forests and sea grass beds, which are critical habitats for a wide range of marine life.
Conservation and Ecosystem Management
The tidal schedule also plays a significant role in the conservation and management of Sanibel Island’s natural resources. The J.N. Ding Darling National Wildlife Refuge, which covers a substantial portion of the island, relies on the tidal patterns to maintain the health and diversity of its ecosystems. The refuge’s mangrove forests, for example, are highly dependent on the tidal flows to bring in nutrients and sediments, supporting a rich biodiversity. Understanding and respecting these natural processes is vital for the long-term preservation of the island’s unique environmental treasures.
Key Points
- The Sanibel Island tide schedule is characterized by a mixed semidiurnal pattern, with two high tides and two low tides of unequal heights each day.
- Understanding the tidal cycles and patterns is essential for planning water activities, shell searching, and fishing.
- The tidal range varies significantly over the course of a month, with the most extreme ranges occurring during spring tides and the least during neap tides.
- Knowledge of the tide schedule is crucial for the conservation and management of the island's ecosystems, including the mangrove forests and sea grass beds.
- Respecting the natural tidal processes is vital for the long-term preservation of Sanibel Island's environmental treasures.
In conclusion, the Sanibel Island tide schedule is a vital component of the island's natural identity, influencing both the human experience and the health of its ecosystems. By understanding and appreciating these tidal patterns, individuals can enhance their visit, contribute to conservation efforts, and ensure the long-term sustainability of this unique and beautiful destination.
How often do the tides change on Sanibel Island?
+The tides on Sanibel Island change approximately every 12 hours and 25 minutes, following a mixed semidiurnal pattern with two high tides and two low tides of unequal heights each day.
What is the best time to search for seashells on Sanibel Island?
+The best time to search for seashells is typically during low tide, when more of the beach is exposed, providing a wider area to explore for shells and other beach treasures.
How does the tide schedule impact fishing on Sanibel Island?
+The changing tides can signal the movement and feeding patterns of various fish species, making certain times more favorable for fishing. Understanding the tidal patterns can increase the chances of a successful catch.