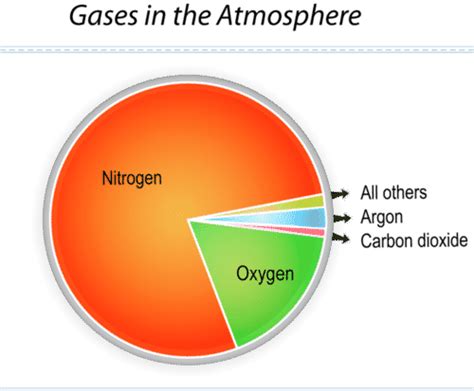
Nitrogen is indeed the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, making up approximately 78.08% of the air we breathe. This inert gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, yet it plays a vital role in the Earth's ecosystem. The high concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere is due to its stable molecular structure, which consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together (N2). This stability, combined with the fact that nitrogen is not readily reactive with other elements, has allowed it to accumulate in the atmosphere over billions of years.
Composition of the Atmosphere

The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases, with nitrogen being the dominant component. The remaining 21.92% of the atmosphere is primarily composed of oxygen (20.95%), with trace amounts of other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. The exact composition of the atmosphere can vary depending on factors such as altitude, temperature, and humidity, but nitrogen remains the most abundant gas throughout. The stability of the atmosphere is crucial for life on Earth, and the presence of nitrogen helps to maintain this balance.
Nitrogen Cycle and Its Importance
Nitrogen is an essential element for life, and its cycle is critical for the health of our planet. The nitrogen cycle refers to the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various forms, including N2, ammonia (NH3), and nitrate (NO3-). This cycle involves the interaction of microorganisms, plants, and animals, and is necessary for the production of amino acids, nucleotides, and other biomolecules. The nitrogen cycle is also closely linked to the carbon cycle, as nitrogen is often a limiting factor in the growth of plants and microorganisms.
| Gas | Percentage Composition |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N2) | 78.08% |
| Oxygen (O2) | 20.95% |
| Argon (Ar) | 0.93% |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | 0.04% |
| Water Vapor (H2O) | Variable |

Key Points
- Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, making up approximately 78.08% of the air we breathe.
- The stability of the atmosphere is crucial for life on Earth, and the presence of nitrogen helps to maintain this balance.
- The nitrogen cycle is essential for the health of our planet, and involves the interaction of microorganisms, plants, and animals.
- Nitrogen is often a limiting factor in the growth of plants and microorganisms, and is closely linked to the carbon cycle.
- The balance of gases in the atmosphere is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystem.
Human Impact on the Nitrogen Cycle

Human activities, such as agriculture and industry, have significantly impacted the nitrogen cycle. The use of nitrogen-based fertilizers has increased the amount of reactive nitrogen in the environment, leading to problems such as eutrophication and air pollution. Additionally, the burning of fossil fuels has released large amounts of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and acid rain. It’s essential to understand the impact of human activities on the nitrogen cycle and to develop strategies for mitigating these effects.
Strategies for Mitigating Human Impact
There are several strategies that can be employed to reduce the impact of human activities on the nitrogen cycle. These include the use of more efficient fertilizers, the implementation of conservation tillage practices, and the reduction of emissions from industrial sources. Education and outreach programs can also play a critical role in raising awareness about the importance of the nitrogen cycle and the impact of human activities on the environment.
What is the most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere?
+Nitrogen (N2) is the most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, making up approximately 78.08% of the air we breathe.
What is the nitrogen cycle, and why is it important?
+The nitrogen cycle refers to the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various forms, including N2, ammonia (NH3), and nitrate (NO3-). This cycle is essential for the health of our planet, as it involves the interaction of microorganisms, plants, and animals, and is necessary for the production of amino acids, nucleotides, and other biomolecules.
How do human activities impact the nitrogen cycle?
+Human activities, such as agriculture and industry, have significantly impacted the nitrogen cycle. The use of nitrogen-based fertilizers has increased the amount of reactive nitrogen in the environment, leading to problems such as eutrophication and air pollution. Additionally, the burning of fossil fuels has released large amounts of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and acid rain.