The Middle East region is home to some of the most critical and contested water sources in the world. The waters of the Middle East are a vital component of the region's ecosystem, supporting agriculture, industry, and human consumption. However, the region's water resources are under significant pressure due to factors such as climate change, population growth, and urbanization. In this article, we will explore the five major Middle East waters, their significance, and the challenges they face.
Key Points
- The Middle East is home to several critical water sources, including the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the Caspian Sea.
- These waters support a wide range of economic activities, including fishing, shipping, and tourism.
- The region's water resources are under significant pressure due to factors such as climate change, population growth, and urbanization.
- Desalination is a crucial component of the region's water supply, with many countries relying heavily on desalination plants to meet their freshwater needs.
- The Middle East waters are also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests.
The Persian Gulf

The Persian Gulf is a vital body of water located in the Middle East, bordering several countries, including Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Oman. The Persian Gulf is approximately 990 kilometers long and 240 kilometers wide, with a maximum depth of about 100 meters. The Gulf is an important shipping route, with many of the world’s largest oil producers located in the region. The Persian Gulf is also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs and sea grass beds.
Significance of the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf is a critical component of the regional economy, with many countries relying on the Gulf for oil exports. The Gulf is also an important source of freshwater, with several desalination plants located in the region. However, the Persian Gulf is facing several challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The Gulf’s coral reefs, for example, are under significant pressure due to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
| Country | Oil Production (barrels per day) |
|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 12,402,000 |
| Iran | 4,503,000 |
| Iraq | 4,451,000 |
| Kuwait | 2,752,000 |
| United Arab Emirates | 2,712,000 |

The Red Sea
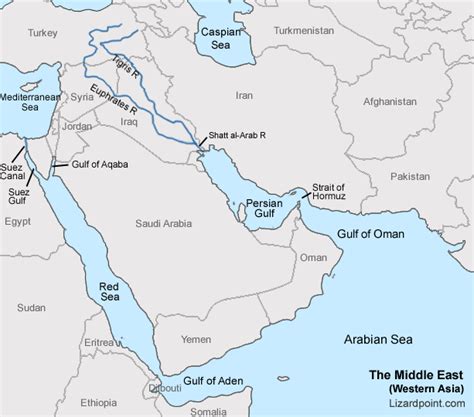
The Red Sea is a body of water located between Africa and Asia, bordering several countries, including Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. The Red Sea is approximately 1,738 kilometers long and 355 kilometers wide, with a maximum depth of about 3,040 meters. The Red Sea is an important shipping route, with many of the world’s largest shipping companies operating in the region. The Red Sea is also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs and mangrove forests.
Significance of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a critical component of the regional economy, with many countries relying on the Sea for oil exports and shipping. The Red Sea is also an important source of freshwater, with several desalination plants located in the region. However, the Red Sea is facing several challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The Sea’s coral reefs, for example, are under significant pressure due to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
The Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a semi-enclosed sea located between Europe, Africa, and Asia, bordering several countries, including Turkey, Greece, Lebanon, Syria, Israel, and Egypt. The Mediterranean Sea is approximately 2,500 kilometers long and 600 kilometers wide, with a maximum depth of about 5,267 meters. The Mediterranean Sea is an important shipping route, with many of the world’s largest shipping companies operating in the region. The Mediterranean Sea is also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests.
Significance of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a critical component of the regional economy, with many countries relying on the Sea for oil exports, shipping, and tourism. The Mediterranean Sea is also an important source of freshwater, with several desalination plants located in the region. However, the Mediterranean Sea is facing several challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The Sea’s coral reefs, for example, are under significant pressure due to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
The Black Sea
The Black Sea is a body of water located between Europe and Asia, bordering several countries, including Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia, and Georgia. The Black Sea is approximately 1,200 kilometers long and 600 kilometers wide, with a maximum depth of about 2,212 meters. The Black Sea is an important shipping route, with many of the world’s largest shipping companies operating in the region. The Black Sea is also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests.
Significance of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a critical component of the regional economy, with many countries relying on the Sea for oil exports, shipping, and tourism. The Black Sea is also an important source of freshwater, with several desalination plants located in the region. However, the Black Sea is facing several challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The Sea’s coral reefs, for example, are under significant pressure due to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
The Caspian Sea

The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed inland body of water in the world, bordering several countries, including Russia, Iran, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan. The Caspian Sea is approximately 1,200 kilometers long and 235 kilometers wide, with a maximum depth of about 1,020 meters. The Caspian Sea is an important source of oil and natural gas, with many of the world’s largest energy companies operating in the region. The Caspian Sea is also home to several important marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests.
Significance of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is a critical component of the regional economy, with many countries relying on the Sea for oil and natural gas exports. The Caspian Sea is also an important source of freshwater, with several desalination plants located in the region. However, the Caspian Sea is facing several challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. The Sea’s coral reefs, for example, are under significant pressure due to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
What are the main challenges facing the Middle East waters?
+The main challenges facing the Middle East waters include pollution, overfishing, and climate change. These challenges are having a significant impact on the region's ecosystems and economies, and require urgent attention and action.
What is the significance of desalination in the Middle East?
+Desalination is a crucial component of the Middle East's water supply, with many countries relying heavily on desalination plants to meet their freshwater needs. Desalination is a significant source of freshwater, and is essential for the region's economic and social development.
What are the main marine ecosystems found in the Middle East waters?
+The main marine ecosystems found in the Middle East waters include coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests. These ecosystems are critical components of the region's biodiversity, and provide important habitat for many species of fish and other marine life.
In conclusion, the Middle East waters are a vital component of the region’s ecosystem, supporting agriculture, industry, and human consumption. However, the region’s water resources are under significant pressure due to factors such as climate change, population growth, and urbanization. It is essential that the region’s governments and stakeholders take urgent action to address these challenges, and work to conserve and protect the Middle East waters for future generations.